The social structure of Sumer represents a complex tapestry of roles, relationships, and hierarchies that defined one of the world's earliest civilizations. This ancient society flourished in the southern region of Mesopotamia, where the Tigris and Euphrates rivers converged. The Sumerians developed a sophisticated system of governance, trade, and cultural practices that reflected their unique social dynamics. Understanding the social structure of Sumer is crucial to grasping how this civilization functioned and influenced subsequent societies in the region and beyond.
At the heart of Sumer's social organization was a system that integrated various classes, from nobles and priests to farmers and laborers. Each group played a significant role in maintaining the stability and prosperity of their city-states. Additionally, the Sumerians' conception of social hierarchy was intertwined with their religious beliefs, as they often viewed their leaders as chosen by the gods. This interconnection between religion and social structure shaped the values and priorities of the Sumerian people.
As we explore the social structure of Sumer, it is essential to examine the various classes that comprised this society and how they interacted with one another. From the ruling elite who wielded political power to the artisans whose skills contributed to Sumer's rich cultural legacy, each class had a unique function that ensured the civilization's success. This article will delve into the intricacies of Sumerian society, highlighting the roles, responsibilities, and relationships that defined this remarkable civilization.
What Were the Main Classes in the Social Structure of Sumer?
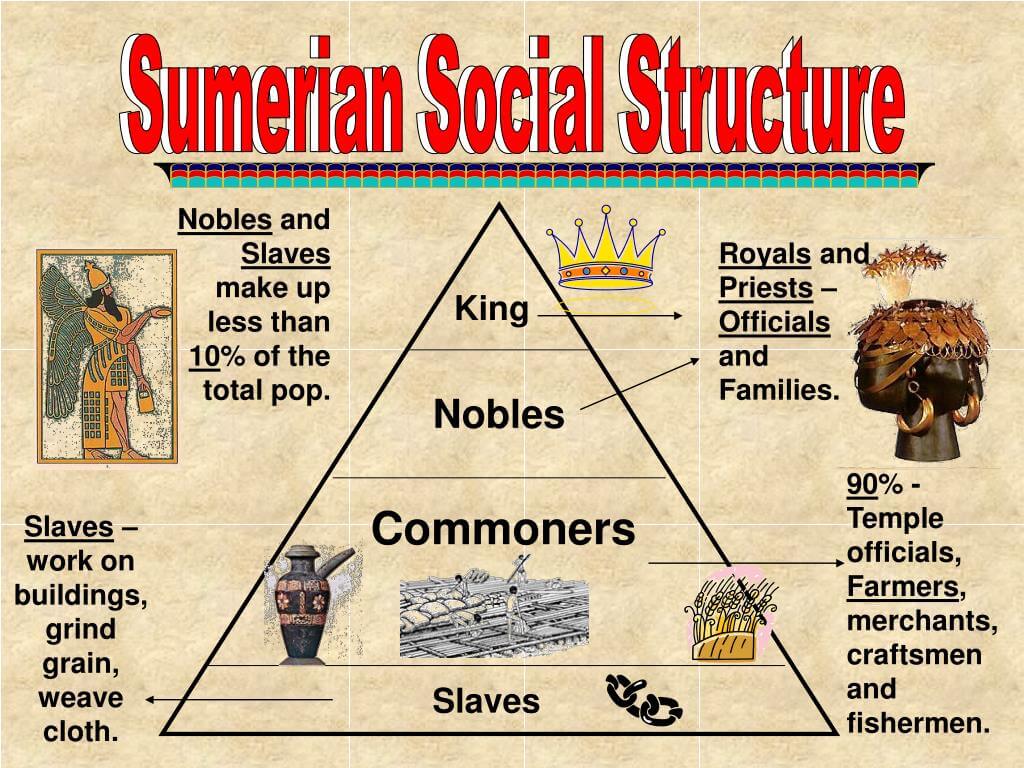
The social structure of Sumer was primarily divided into three main classes: the ruling class, the middle class, and the lower class. Each of these classes had its own distinct roles and responsibilities within the community.
- Ruling Class: This elite class comprised kings, priests, and nobles who held significant political and religious authority. They made important decisions regarding governance, warfare, and religious rituals.
- Middle Class: The middle class consisted of merchants, artisans, and skilled laborers. They played a crucial role in trade and the economy, contributing to the development of Sumer's cities.
- Lower Class: This class included farmers, laborers, and slaves who performed essential manual labor. They were the backbone of Sumer's agricultural economy.
How Did Religion Influence the Social Structure of Sumer?
The social structure of Sumer was deeply intertwined with religious practices and beliefs. The Sumerians were polytheistic, worshiping a pantheon of gods and goddesses who were believed to control various aspects of life. Religion was not just a personal belief system; it was a fundamental aspect of Sumerian identity and governance.
Priests, who were part of the ruling class, held significant influence over society. They acted as intermediaries between the gods and the people, conducting rituals and ceremonies to ensure divine favor. The temples, known as ziggurats, served as both religious centers and administrative hubs, further solidifying the connection between religion and governance.
What Roles Did Women Play in the Social Structure of Sumer?
Women in Sumerian society experienced varying degrees of freedom and influence depending on their social class. While the patriarchal structure dominated, women were not entirely relegated to the background.
- Elite Women: Women from the ruling class often held significant power, sometimes serving as priestesses or even rulers in their own right.
- Middle-Class Women: These women could engage in trade and own property, contributing to the family's economic well-being.
- Lower-Class Women: While their roles were primarily domestic, they played a vital part in the agricultural sector and family life.
How Did Trade Impact the Social Structure of Sumer?
The Sumerians were adept traders, establishing extensive networks that connected them with neighboring regions. The flourishing trade contributed significantly to the social structure of Sumer, as it facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and culture.
Trade allowed the middle class to prosper, leading to an increase in wealth and influence. Merchants became crucial players in the economy, often amassing considerable fortunes. This newfound wealth sometimes enabled them to ascend the social ladder, blurring the lines between the upper and middle classes.
What Role Did Agriculture Play in the Social Structure of Sumer?
Agriculture was the lifeblood of Sumerian society, forming the foundation of their economy and social structure. The fertile land along the Tigris and Euphrates rivers allowed for bountiful harvests, which supported the population and facilitated trade.
- Farmers: The vast majority of the population consisted of farmers who worked the land. Their labor was essential for sustaining the community.
- Laborers: Many laborers were employed in constructing irrigation systems, canals, and city walls, further enhancing agricultural productivity.
How Did Warfare Affect the Social Structure of Sumer?
Warfare was a recurring theme in Sumerian history, as city-states often competed for resources and territory. The impact of warfare on the social structure was profound, leading to shifts in power and influence among the classes.
Military leaders often ascended to positions of authority, and successful campaigns could enhance a city's prestige and wealth. However, the consequences of warfare also placed a heavy burden on the lower class, who were frequently called upon to serve as soldiers or laborers in wartime efforts.
What Legacy Did the Social Structure of Sumer Leave Behind?
The social structure of Sumer laid the groundwork for future civilizations in the region. Its hierarchical organization, coupled with the integration of religion, trade, and agriculture, influenced the development of subsequent societies, including the Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians.
As we study the social structure of Sumer, we gain insights into how complex societies can evolve, adapt, and shape the course of history. The lessons learned from Sumer's social dynamics continue to resonate in modern discussions about governance, class, and social organization.
Also Read
Unveiling The Legendary Ian Paice: A Drumming IconKardashian Bums: The Cultural Phenomenon That Redefined Beauty Standards
Unveiling The Life And Career Of Beth Ostrosky
Navigating The Ocean: Understanding NYC To London Nautical Miles
Understanding The Decline Of Vision: Eyesight Getting Worse In Your 20s
Article Recommendations
- La Freeway Protest
- 1470855 Zack Lugos Biography Age Height Net Worth Girlfriend Brother
- 1230857 Tyler Perry Net Worth Age Height House Wife Son
- Thay Ksada
- Oleksandr Zinchenko
- Kristy Mcnichol
- Josh Allen Old Tweets
- Tiffany Link Earrings
- 1534693 Piece Female Characters Deserve Attention