The Sumer civilization, known for being one of the world's earliest urban societies, was remarkable not just for its innovations in writing, agriculture, and governance but also for its complex social structure. Understanding the Sumer social structure provides insights into how this ancient society functioned and thrived. The Sumerians established a hierarchy that was both rigid and multifaceted, influencing every aspect of daily life, from governance to labor distribution and even religious practices.
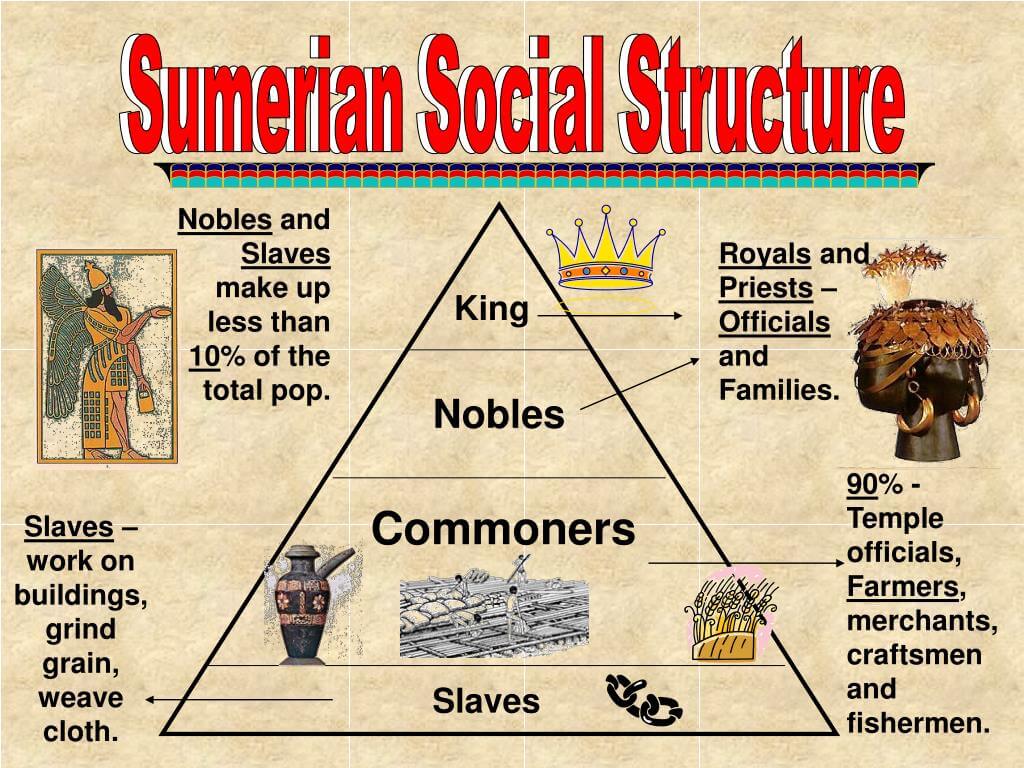
The Sumer social structure was characterized by distinct classes that defined one's role and status within the community. At the top of this hierarchy were the ruling elites, including priests and kings, who wielded significant power and authority. Below them were the free citizens, who were typically skilled laborers and artisans, while at the bottom of the social ladder were the slaves, often prisoners of war or individuals in debt. This stratification was not just a reflection of wealth but also of the responsibilities and roles that each class played in sustaining the city's economy and culture.
By examining the Sumer social structure, we can better appreciate the dynamics that allowed this civilization to flourish for centuries. Their social organization was crucial for maintaining order, facilitating trade, and ensuring the continuation of cultural and religious practices. This article delves deeper into the various classes within Sumerian society, their roles, and the impact of this structure on the civilization as a whole.
What Were the Main Classes in the Sumer Social Structure?
The Sumer social structure was typically divided into four main classes, each with its own distinct roles and responsibilities:
- Ruling Class: This class included the kings, priests, and nobles who held political and religious power.
- Free Citizens: Skilled workers, merchants, and landowners who contributed to the economy and social fabric of Sumer.
- Commoners: Farmers and laborers who performed essential tasks to support the city-state.
- Slaves: Individuals who were bound to serve others, often as a result of war or debt.
How Did Religion Influence the Sumer Social Structure?
Religion played a pivotal role in Sumerian society, shaping not only cultural practices but also the social hierarchy. The priests were among the most powerful figures in Sumer, acting as intermediaries between the gods and the people. Their influence extended beyond the religious sphere into political matters, as many kings claimed divine right to rule, legitimizing their authority through religious practices.
What Role Did the King Play in the Sumer Social Structure?
The king in Sumer was not just a political leader but also a religious figure. His responsibilities included:
- Maintaining the favor of the gods through rituals and offerings.
- Ensuring justice and order within the city-state.
- Overseeing the administration and defense of the realm.
This duality of kingship reinforced the social structure, as the king's power was both divinely ordained and politically necessary for the stability of Sumerian society.
How Were Free Citizens and Commoners Organized?
Within the ranks of free citizens and commoners, there was a degree of organization that allowed for efficient functioning of the urban economy. Artisans and merchants often formed guilds, which regulated trade practices and set standards for their respective crafts. This organization helped to elevate the status of skilled workers and provided a means of support for those in the lower classes.
What Was the Impact of Sumer Social Structure on Daily Life?
The Sumer social structure had profound implications for daily life. It dictated everything from job roles to marriage customs, and even religious observances. The distinctions between classes influenced how resources were allocated, how education was accessed, and how social mobility was perceived. For example:
- Education was primarily reserved for the elite, further entrenching social divisions.
- Marriages were often arranged to strengthen alliances between families of similar status.
- Religious festivals and ceremonies were significant events that reinforced social hierarchies, with the ruling class often taking center stage.
How Did the Sumer Social Structure Evolve Over Time?
As Sumerian city-states grew in power and complexity, so too did their social structure. Over time, new classes emerged, such as merchants and traders, who gained wealth and influence through commerce. This evolution led to shifts in the power dynamics within Sumer, as the traditional ruling class had to adapt to the changing economic landscape.
What Legacy Did the Sumer Social Structure Leave Behind?
The legacy of the Sumer social structure is evident in many aspects of modern society. The concepts of governance, law, and social organization can trace their roots back to the Sumerians. Their innovations in writing, particularly cuneiform, allowed for record-keeping that facilitated trade and administration, laying the groundwork for future civilizations.
In Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Sumer Social Structure
In summary, the Sumer social structure was a complex and integral part of one of the earliest civilizations in human history. By understanding its intricacies, we gain valuable insights into the social dynamics that have shaped human society over millennia. The stratification of Sumerian society not only defined individual roles but also influenced the development of culture, religion, and governance in ways that continue to resonate today.
Also Read
The Intricate Tapestry Of Sumer Social StructureExploring The Distance: How Far Is London From NYC?
Exploring The Organic Nature Of Trader Joe's Flowers
Are Pedro Pascal And Paul Mescal Related? Unraveling The Connection
Discovering The In N Out Ticker Symbol: A Fast Food Phenomenon
Article Recommendations
- 1230857 Tyler Perry Net Worth Age Height House Wife Son
- Tiffany Link Earrings
- 1534693 Piece Female Characters Deserve Attention
- La Freeway Protest
- Thay Ksada
- 1470855 Zack Lugos Biography Age Height Net Worth Girlfriend Brother
- Kristy Mcnichol
- Josh Allen Old Tweets
- Oleksandr Zinchenko